In today’s dynamic business landscape, understanding the concepts of market orientation and product orientation is crucial for organisations aiming for long-term success. A market-oriented company is one that structures its activities, products, and services around the wants and needs of its customers. In contrast, a product-oriented firm primarily focuses on its products, emphasising the skills, knowledge, and systems that support those products.
Historically, many companies leaned heavily towards product orientation until the late 20th century. This focus on product development often led to a disconnect with the evolving needs of consumers in an increasingly competitive marketplace. However, the paradigm has shifted significantly, with a pronounced movement towards market orientation that has resulted in intensified market research and product ranges meticulously designed to align with customer preferences.
The Shift Towards Market Orientation
The shift from product orientation to market orientation is a reflection of changing consumer behaviours and heightened competition. In the past, companies that focused solely on their products often misjudged market demand and customer expectations. As markets became more saturated, the importance of understanding consumer needs became paramount.
Today, businesses are increasingly recognising that a thorough understanding of the market is essential for success. Market orientation involves a comprehensive approach to identifying and responding to customer preferences, which can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Companies that adopt this orientation prioritise customer feedback, engage in regular market research, and continually adjust their offerings based on insights gleaned from consumers.
The rise of digital technologies and social media has further amplified the importance of market orientation. Consumers now have greater access to information and are more empowered than ever to voice their opinions about products and services. Businesses must stay attuned to these shifts to remain competitive, which has led to a focus on gathering and analysing customer data to inform decision-making processes.
The Role of Product Orientation
While the shift towards market orientation is undeniable, product orientation still holds significant importance, particularly in certain contexts. Product-oriented firms emphasise the quality, safety, and technological advancement of their offerings. This focus can lead to the development of innovative products that set a company apart from its competitors.
For example, companies that invest heavily in research and development (R&D) are often able to produce cutting-edge products that appeal to consumers. A strong product orientation ensures that the products meet rigorous quality standards and comply with safety regulations, which can enhance a brand’s reputation and foster consumer trust.
In certain industries, particularly those driven by technological advancements, product orientation is vital. Companies in sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and automotive manufacturing must continually innovate to stay ahead of the competition. In these cases, a robust product orientation can drive growth and profitability by ensuring that the products meet or exceed market expectations.
Finding the Balance: Integration of Market and Product Orientation
Successful companies recognise the importance of integrating both market and product orientation. The most effective strategies involve understanding customer needs while simultaneously ensuring high-quality production. This dual focus can lead to the development of products that not only meet market demand but also exceed expectations in terms of quality and performance.
To illustrate this integration, consider how leading companies operate:
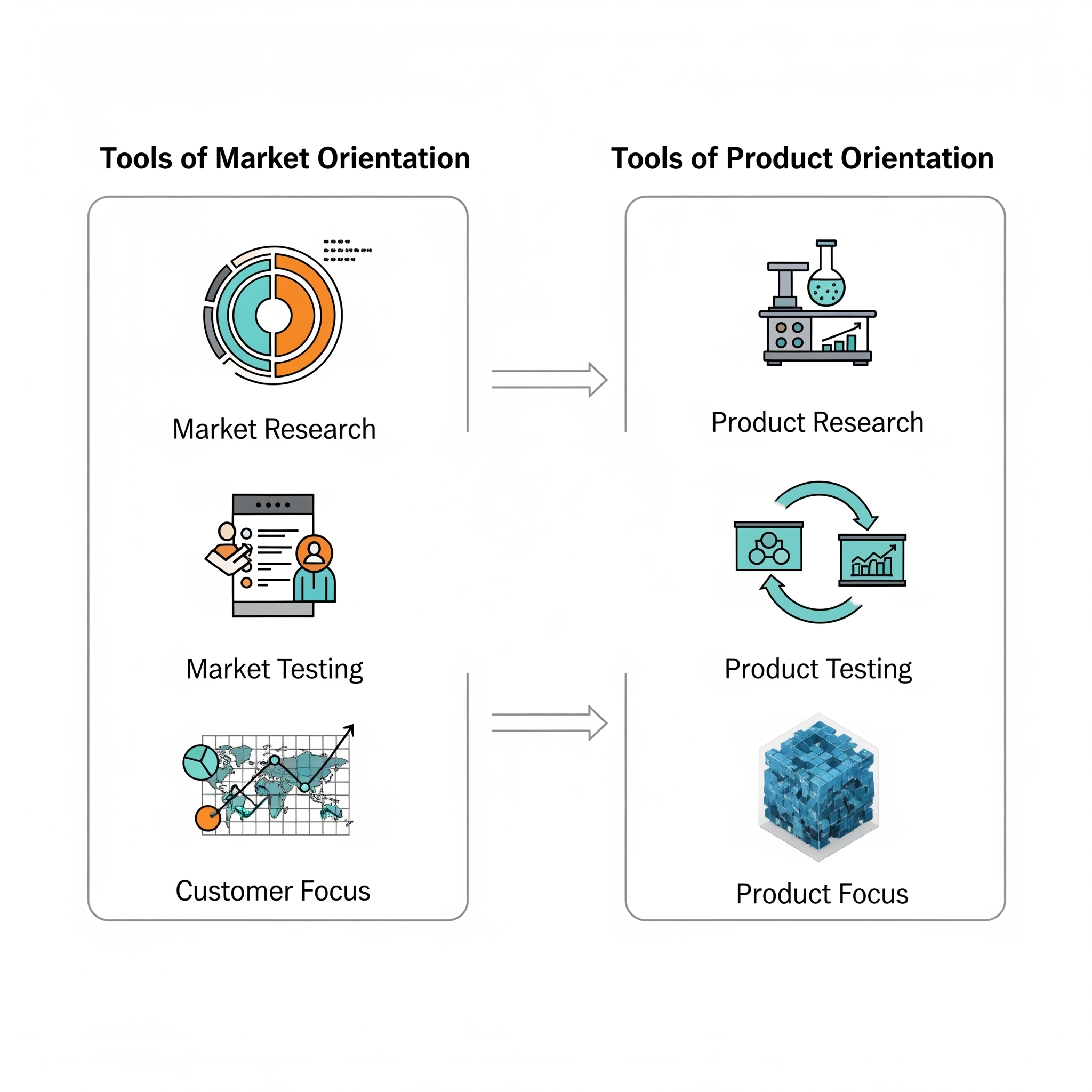
- Market Research: Companies such as Gillette, Coca-Cola, and Travis Perkins conduct extensive market research to identify consumer preferences. This research involves collecting data on customer needs, behaviours, and trends, which provides valuable insights for product development.
- Product Development: Based on the findings from market research, these companies organise product research to align new offerings with consumer preferences. This step ensures that products are designed to meet market demands effectively.
- Qualitative Market Research: Continuous engagement in qualitative market research is essential. Focus groups are often employed to gather insights from customers regarding new ideas or product modifications. This feedback is invaluable in refining products and ensuring they resonate with the target audience.
- Test Marketing: Before launching new products on a larger scale, successful companies typically test market their offerings in smaller, controlled environments. This allows them to gauge consumer reactions and make necessary adjustments based on real-world feedback.
- Ongoing Evaluation: Post-launch, companies evaluate customer perceptions of their goods and services regularly. This ongoing assessment enables businesses to identify areas for improvement and adapt their technologies and product offerings accordingly.
Market Orientation vs. Product Orientation: A Complementary Approach
The relationship between market orientation and product orientation can be viewed as complementary rather than mutually exclusive. While market orientation ensures that the right product is developed to meet consumer needs, product orientation focuses on delivering that product with exceptional quality.
To elaborate on this, let’s consider a practical example. A company that manufactures athletic footwear may begin by conducting market research to understand consumer preferences regarding style, comfort, and performance. This research may reveal a growing demand for eco-friendly materials and customisation options.
In response, the company can employ its product orientation to invest in R&D aimed at developing sustainable materials and innovative manufacturing processes that allow for personalised designs. By combining insights from market research with a commitment to quality and innovation, the company can launch a product that meets consumer expectations while maintaining high production standards.
Challenges of Balancing Both Orientations
Despite the clear benefits of integrating market and product orientations, companies often face challenges in achieving this balance. For instance, businesses that are heavily entrenched in product orientation may struggle to pivot towards a more market-driven approach. This inertia can stem from organisational culture, resistance to change, or a lack of understanding of market dynamics.
Conversely, companies that prioritise market orientation may inadvertently overlook the importance of product quality. If a business focuses solely on consumer trends without ensuring that its products are of high quality, it risks damaging its reputation and losing customer trust.
To overcome these challenges, organisations must foster a culture that values both market insight and product excellence. This involves training employees, promoting cross-functional collaboration, and establishing feedback loops that allow for continuous improvement in both areas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the interplay between market orientation and product orientation is a crucial factor in determining a company’s success in today’s competitive landscape. While market orientation allows businesses to align their products and services with customer needs, product orientation ensures that these offerings are of the highest quality.
To thrive in the market, companies must embrace both approaches, recognising that the right product delivered with excellence can significantly enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. By integrating market research with robust product development, businesses can create innovative solutions that resonate with consumers and maintain a competitive edge.
Ultimately, the most successful companies are those that recognise the importance of both market and product orientation, leveraging their strengths to navigate the complexities of modern consumer behaviour and preferences. Through continuous evaluation and adaptation, these organisations can not only meet market demands but also drive industry innovation and growth.