
Inventions, literary works, music and design are all intangible assets. The legal right to these ‘creations of the mind’ is referred to as Intellectual Property (IP). ARM Holdings is the world’s leading semiconductor Intellectual Property (IP) supplier. A semiconductor is an electronic controller at the heart of many devices that we use every day, such as Smartphones, tablets, digital televisions and washing machines. In fact, ARM IP is at the heart of 35% of all consumer devices worldwide.
ARM has an innovative business model. ARM does not manufacture the products in which its technology is used. Instead, ARM creates the technology that is then used by other companies – its partners. These partners incorporate ARM IP with their own technology to create smart, energy-efficient chips suitable for modern electronic devices. ARM licenses its IP for a one-off licence fee and then receives royalty fees for every chip that contains its technology. ARM effectively acts as an outsourced research and development (R&D) department to its network of partners.
With its headquarters in Cambridge (UK) and offices around the world, ARM employs over 2,500 highly skilled people. To maintain its market leading position, ARM carefully monitors changes in its external environment to ensure it can continue to outperform its competitors. Analysing these changes allows ARM to establish opportunities, threats and challenges. Key opportunities for growth include:
- Advancements in technology – including machine-to-machine communications between smart sensors, referred to as ‘The Internet of Things’. For example, appliances in the home can be monitored and controlled wirelessly by the homeowner wherever they are.
- Market development – increasing market share in new markets such as servers and networking equipment. ARM’s technology is well placed to provide lower power options to transport, distribute, analyse and store data across the internet.
- Demand for energy efficient technology – the market demands high performance products using low power technology.
This case study will demonstrate how ARM’s strategies contribute to the achievement of its business vision, aims and objectives using an integrated approach focusing on innovation, its people and its network of partners.
Vision aims and values
An organisation’s vision outlines what the company wants to achieve. A vision should be aspirational and inspirational for stakeholders, especially employees. ARM’s vision is:
‘To create a world where all electronic products and services, based upon energy efficient technology from ARM, make life better for everyone.’
This vision will affect every aspect of the business. All strategic decisions will be geared towards making this vision a reality. To help deliver the vision, an organisation will set aims. Aims describe what the business intends to do in the long term. In order to achieve its vision, ARM aims to:
- attract and retain the best talent globally
- continue to grow the business to ensure maximum revenue to develop new technologies through R&D and also deliver funds to shareholders
- promote collaboration and shared learning through its network of partners.

ARM’s biggest asset is its people. Due to the knowledge-intensive nature of the business, ARM relies on its innovative and highly skilled employees to maintain its market leading position. Maintaining its highly motivated workforce is therefore a key aim. To aid the achievement of its aims, ARM has set seven core business values. A company’s values demonstrate the things it deems to be of the utmost importance. These values underpin everything that the company does. ARM’s core values include:
- Teamwork and selflessness – sharing information and knowledge openly both internally and externally.
- Constructive pro-activity – developing practical solutions with a ‘can do’ approach.
- Partner and customer focus – understanding their needs.
- Responsiveness – always reacting with a sense of urgency.
- Innovation – developing practical solutions to problems.
- Personal development – through training, coaching and mentoring.
- Delivery of results – using expertise to benefit ARM.
These ARM values support the achievement of its vision and aims. They also complement its business model and demonstrate the company’s focus on its workforce. An organisation’s vision aims and values all influence the development of plans for the future direction of the company, namely its business strategies.
Strategy
A business strategy is a plan by which aims and objectives will be put into action. Objectives are the specific targets to achieve the aims. Without business strategies, in place, an organisation will not have a clear direction so would be more likely to fail. ARM has a number of strategies in place to achieve its aims and contribute towards its vision. These include strategies related to growth, Human Resources (HR) and its network of partners.
ARM has seen dramatic growth in recent years. To continue to expand the business ARM has identified three main drivers for growth which are identified in the table. By focusing on these three areas, ARM aims to continue to grow and maximise revenue.
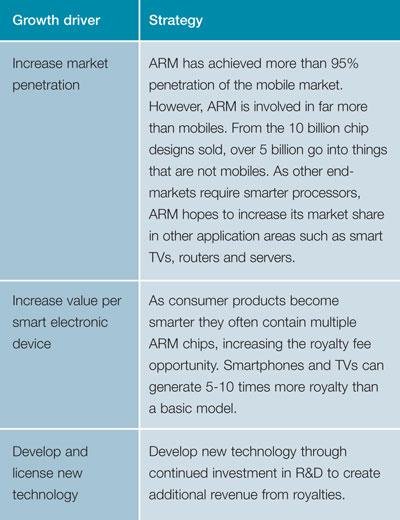
ARM HR strategies support its growth strategies. By attracting and retaining people with high levels of skills and expertise, ARM can continue to develop the competencies which give it a competitive advantage and enable it to drive its vision forward. To do this ARM’s HR team must ensure a pipeline of talent through workforce planning and recruitment. Training and development opportunities also help to ensure a motivated workforce that will ‘live’ ARM’s values.
Dramatic growth has meant the ARM workforce has increased by 40% in the past three years. As over 80% of ARM employees are educated to a degree level or higher, this growth has created a challenge for the ARM HR team. During workforce planning, gaps can arise between what ARM wants to achieve (its objectives) and the resources available to achieve them. These strategic gaps are dealt with through Human Resource Management (HRM). One such strategic gap is attracting sufficient young people with scientific skills to meet the growing needs of the business. To overcome this gap ARM promotes the importance of science, technology, engineering and maths (STEM subjects) to young students.
The ARM ecosystem strategy supports its business model. ARM’s people develop effective relationships with over 1,000 companies that license ARM technology. The working environment that ARM has created is referred to as its ecosystem of partners. These relationships stimulate innovation between companies to develop the next generation of products. As well as attracting new partners, a large amount of growth occurs when existing partners upgrade their ARM processors to the next generation. This strategy directly supports ARM’s vision and its aim of shared learning.
Delivering a strategy
Behind every business strategy are tactics. Tactics are the means by which the strategy will be implemented. Objectives, which can be set at a function level or for the whole business, outline the outcomes the business needs in order to achieve its aims. The SMART objectives model helps ensure that objectives are achievable. It states that the objectives should be:
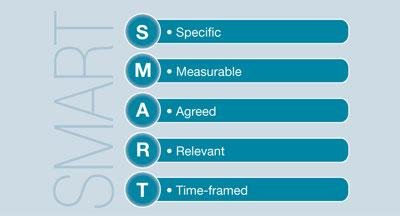
Through the setting of SMART objectives, ARM is able to plan for the future to aid the achievement of its business strategies. ARM SMART objectives are influenced by many factors, for example, the innovative and technical nature of the business requires a highly skilled workforce. A functional objective for its HR strategy is that 30% of new recruits in 2013 will be graduates. This figure will increase to 40% in 2015 and 50% by 2017. A tactic that supports this objective is that ARM has a strong presence at the leading universities’ careers fairs around the world. It also runs a two-week Global Graduate Conference that enables new graduates to become more effective in a shorter space of time. This objective and tactic supports its business aim to attract and retain the best talent globally, as well as promoting the company’s value of personal development.

Another ARM SMART objective is to have an overall market share of between 40% and 50% by 2017. In 2012 ARM’s market share was 32%, an increase of 2% to 3% per year for the last five years. The growth drivers of increasing market penetration and value per smart electronic device support this objective, and as ARM partners use ARM technology in more of their products the company’s market share is set to continue to grow.
In relation to increasing penetration in new markets, a SMART objective has been set that by 2017 ARM aims to have a 10% to 15% share of the IT server market. This supports the growth strategy of market penetration. Networking servers are a new market where ARM technology is increasingly being used by its partners, however, ARM has no market share. To evaluate and test its technology in this market ARM invested in R&D throughout 2012. This enabled ARM to generate technology used in several commercial products in 2013.
Culture

As well as external factors, many other factors within an organisation have a huge impact on its business strategies. Every organisation has a typical way of doing things, known as the organisation’s culture. This particularly relates to employees’ behaviour patterns and relationships. A culture is not developed overnight, it takes time to build and will be heavily influenced by the organisation’s vision and values.
ARM’s culture is one of honesty and accountability. This in turn creates trust amongst its employees and stakeholders and supports its values of team building and its ‘can do’ approach. The leadership at ARM creates a supportive working environment by using its personal development and ecosystem strategies to maximise employee potential and innovation.
ARM Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives both reflect and enhance the company’s culture and HR strategies. CSR involves taking into account the wider needs of society to ensure the business has a positive impact. In 2012, ARM set a CSR objective to develop relationships with charities to create long-term value for both the charity and ARM. This was achieved using the following tactics:
- ARM entered into partnerships with Code Club and the Raspberry Pi Foundation to encourage the development of skills in computer programming and STEM subjects among young people.
- ARM is committed to helping both causes through financial and mentoring support.

ARM’s involvement with Code Club and the Raspberry Pi Foundation aims to increase children’s and young adults’ exposure to computer programming and the opportunities available through studying STEM subjects. It is hoped that this will help develop the necessary skills to be technology leaders of the future. This demonstrates how ARM CSR activities bring benefits to both the charities and ARM’s HR strategies of workforce planning.
Conclusion

In a technology driven industry, ARM IP allows its partners to meet the demands of their markets. As consumers expect more and more from the performance of their digital devices, ARM technology creates innovative solutions that enable its network of partners to meet these demands.
ARM’s vision, culture and values, coupled with clear, well-defined strategies, have enabled the company to maintain its market leading position in its core markets whilst experiencing dramatic growth in several new areas. Its focus on its workforce and its ecosystem of partners have created a culture of trust and open communication where individuals and innovation can thrive to create the technological products of the future. These benefit the company’s key stakeholders, partners and society in a sustainable way that few other companies can compare with.
