Market research is a systematic process used by a business to find out about its customers and its markets. A company uses market research to ensure that it offers goods and services that customers want to buy. This should be a continuous process. Once a product is launched, it is important to listen to customer feedback. By acting on this feedback, businesses can help to keep customers satisfied.

Market research is as important for service industries, such as banking, as it is for manufacturing. This case study features first direct, a member of HSBC Bank. first direct has its own brand identity and its own product range. It attracts customers who want the convenience of telephone and online banking and who are comfortable with using modern technology to access bank services. These customers seek greater control of their money and are more confident about making financial decisions.
first direct launched in 1989. It offered a new type of banking service. Customers could access all banking services by telephone. The bank was open 24 hours a day, seven days a week, 365 days a year (a 24/7/365 service), with real people always on the end of the phone. This contrasted with the services then offered by the major high street banks. These were available only in traditional banking hours, usually 9am to 4pm. The banks closed for most of the weekend. Most transactions had to be made face-to-face. It was difficult to contact the bank unless customers visited a branch.
first direct”s service became highly popular with its customers. The bank won many awards for its service model. By offering additional services such as internet banking and mobile (on the move) banking, customers could access their accounts and manage their money whenever and wherever they liked. However, it was not just about the fact that it was convenient, but also that the people at first direct were courteous, friendly, professional and adult-to-adult.
Competitive advantage
When it launched, first direct was unique. By 2000, however, rival banks were providing similar channels of communication. Banks like Cahoot, Egg and Smile also offered the same type of service and competed strongly on price. first direct was losing some of its competitive advantages.
This case study shows how first direct has used market research to revitalise its brand. It took action following a period in which it was losing customers to other banks.
By taking action, first direct aimed to regain its position as Britain”s most recommended bank.
Understanding the market

A business must understand the market that it operates in. It must understand its customers, so that it can provide the goods and services they want. It must know about its competitors. Businesses that fail to match or better the products, prices and service standards offered by competitors will lose customers. This is what happened to first direct for a period. The bank changed some of its terms and conditions, in order to deepen customer relationships and to encourage more usage of the bank. For example, current account customers paying in less than £1,500 a month (and not having other first direct products) were charged a fee. This was a bold move in a banking market in which most individuals did not expect to pay for having a current account.
The initial response to these changes was not encouraging. The media picked up the story and the resulting publicity affected the bank”s reputation for good customer service.
first direct undertook research through a market research agency. This showed that customer perceptions of first direct had dipped. The survey measured the percentage of customers satisfied with the bank at which they held their main current account. first direct was no longer the top-performing bank by this measure.

first direct therefore decided to carry out further market research to identify how to restore the brand. The bank wanted this research to help it:
- assess if its products and services were the right ones for customers
- identify how first directis viewed in comparison with its rivals
- create ideas about how to improve customer awareness, to retain the loyalty of customers and to develop the business
The market research process
Market research is the collection and analysis of information about a business”s markets. This can cover features such as market trends, customer behaviour and opinions and the business strategies of competitors. Its purpose is to help a business decide its marketing mix. This is sometimes known as the four Ps:

Types of research
There are different types of market research. One important classification is between primary research and secondary research.
- Primary research involves commissioning new research. It involves collecting information directly from customers (and potential customers).
- Secondary research draws on existing information on the market. It involves compiling information from government statistics, sales data, reports by industry analysts and articles in the trade and business press. This is also known as “desk research”.
There are advantages and disadvantages to each approach:
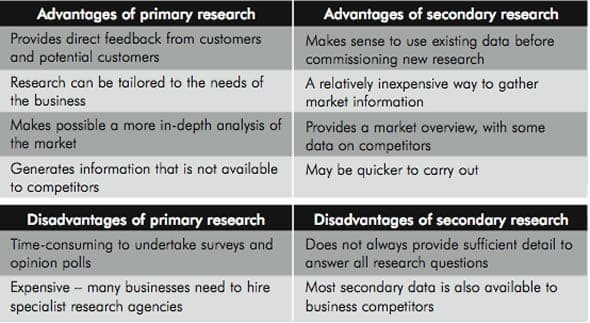
Another important difference in market research is between quantitative and qualitative research. Quantitative research generates numerical information, such as data on the size of the market and the percentage of customers satisfied with a particular product. Qualitative research provides explanations for customers” opinions and behaviour. It provides information on why people like or dislike a product.
Ways of obtaining information

first direct used a variety of primary research methods as it prepared to relaunch its brand. This was a staged process. It sought customers” opinions on its current products and services. Then, as it considered changing its service proposition its product range and marketing mix it tested new ideas with groups of customers and potential customers. Testing gives direct feedback on how customers will respond before launching a service, as well as providing guidance on the most appropriate proposition.
The bank used focus groups and in-depth interviews to gain an understanding of consumer responses to the proposition at each development stage. This was followed by quantitative research to provide representative findings. This involved online questionnaire surveys of large groups of both customers and potential customers.
The focus groups provided qualitative information about customer perceptions and expectations. For example, customers wanted first direct to provide a fair banking service, with a transparent set of charges.
The surveys also provided first direct with quantitative data about its products. For example, it found that 96% of customers felt that credit interest was not an important factor in choosing to bank with first direct. In fact, almost 70% did not know the interest rate on their current account.
Outcomes of the market research

One insight gained from the market research was that some customers had very different opinions about first direct. There were two key customer segments with very different ideas.
The discussions in the focus groups showed that customers wanted first direct to be fair and transparent. They should be able to see what they were getting and there should be no hidden charges. The key brand value 24/7/365 availability was still very important. However, customers also expected first direct to be different from other banks. They wanted the bank to provide innovative services.
As well as providing information on how to position the brand, the research also allowed first direct to test the reaction to specific product proposals. This means the company found out how customers felt about new product ideas. In this way, it informed the product development process.
Revitalising the brand

This process of brand positioning and product development through a programme of extensive market research enabled first direct to relaunch the brand. In doing so, it made adjustments in its marketing mix.
Place is a key component of this mix. When first direct launched it offered banking services to customers who did not want to be tied to visiting a branch during opening hours. It continues to offer 24/7/365 accessibility. It supports different channels to access services including web, text and phone banking. It continues to develop these services. Banking can now be carried out by iPhone.
New products have been introduced and some discontinued. The bank no longer offers interest on current accounts. Instead it offers a new “1st Account” that combines a current account and the option of a linked savings account. These allow positive balances on current accounts to be transferred regularly to savings. This means the customer receives a higher rate of interest on money in the savings account.
It has introduced new products to its savings portfolio. These include:
- Everyday e-Saver accounts customers with a positive savings balance receive a competitive rate of interest
- Regular Saver accounts these give high interest rates for 1st Account customers. The two new savings products generated 10,862 new accounts on the first day of sales
The bank has also sought to be more competitive on price by reducing the cost for some services. For example, it offers 0% interest on overdrafts up to £250 and provides free text alerts to warn customers if their account is nearing their limit. In addition to the product changes, first direct redesigned the visual elements of the brand. This included the logo, the look and feel of all promotional material as well as the interiors of the call centres.
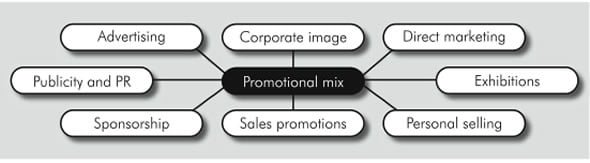
first direct also reconsidered its promotional mix. Promotion is the means used to inform customers about services and to encourage them to buy products. There are a range of tools that can be used for this purpose.
first direct started by promoting the rebranding to its staff. For the business” 18th birthday celebration, all staff were given birthday gifts themed to demonstrate the relaunch. The gifts included rucksacks, security pass-holders, mouse mats, t-shirts and celebratory champagne and chocolates. This helped to ensure employees were fully aware of the new design and messages and would be able to talk confidently about them to customers.
Above-the-line promotion
Advertising is referred to as above-the-line promotion. This type of promotional activity is usually paid for. To support the relaunch, first direct commissioned:
- television advertising campaign
- posters on the London underground
- branded London taxis, with a free ride if the passenger was a first direct customer
- a press campaign, which included advertisements in magazines and newspapers
Below-the-line promotion
Other types of promotional activity are referred to as below-the-line promotion. This type of promotion is more within the business” control and can be more easily measured. These activities used to promote the relaunch included:
- direct calls to key customers to tell them about what was on offer
- personalised letters for customers
- new corporate branding, with a clearly differentiated logo from HSBC
- good quality information materials
In addition, first direct undertook some public relations (PR) activity. It sent out clearly worded press releases to the media. A DVD was issued to support the relaunch. This was sent out to all stakeholders, that is, everyone with an important interest in the company.
Conclusion

first direct has always been a pioneering bank. It creates convenience, setting it apart from competitors. For a short while, first direct lost its way and became more like other banks. Fortunately it understands the importance of market research and marketing. It asked customers what they wanted. The answers were clear and so was the response. first direct is now recapturing its distinctive reputation in the banking sector.
